Microbial EV Nanotherapeutics
That commensal bacteria play an essential role in human health is beyond doubt, and it is now widely accepted that humans are holobionts whose collective metabolic potential exceeds the sum of the individual eukaryotic and prokaryotic components. Probiotics or live biotherapeutics (LBPs) are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host and are widely used in many countries in clinical practice. Paraprobiotics are currently referred to as “modified probiotics”, “inactivated probiotics”, “nonviable probiotics”, or “ghost probiotics”.
Product Details
Paraprobiotics are a newly emerging modality, an immobilized version of probiotics that has gained traction in recent years due to concerns about the possibility of low tolerance of probiotics or LBPs, especially in pediatric populations and severely ill or immunocompromised patients. However, the mechanism of action (MoA) of LBPs and parabiotics is not well understood, although the possible MoAs include immune system regulation and interference with pathogen attachment to host cells.
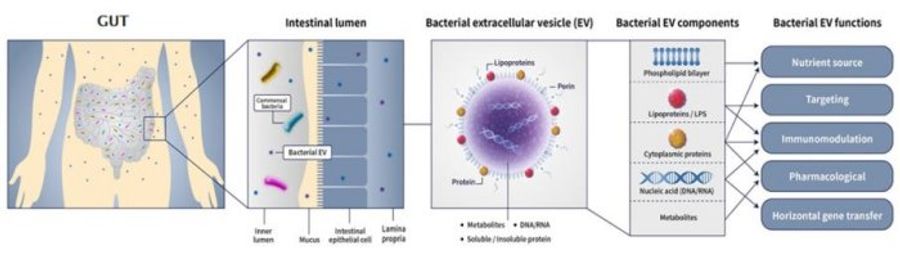
Postbiotics, also known as metabiotics, biogenics, or simply metabolites, refer to soluble factors and EVs secreted by live microbes or released after microbial lysis, and they provide physiological benefits to the host. Postbiotics are a newly emerging modality in therapy. Cell-to-cell communication is tightly regulated, and its disruption contributes to disease development. Intercellular communication can occur either via cell-to-cell contact or via soluble factors. Soluble factors include proteins and small molecules that bind specific receptors on target cells, which then trigger a signaling cascade that will affect the cell phenotype. However, more recently, another process also involved in this type of communication has been highlighted. In addition to producing specific factors, microbial cells can send a package of information, called microbial EVs, that is enclosed by a cell membrane. Moreover, recent scientific evidence has shown that certain microbial EVs have protective effects against disease development or progression.
Microbial EVs are commensal nonliving materials that act on the human immune system to induce protective responses. Microbial EVs are absorbed into and distributed in various organs after oral administration. Furthermore, microbial EVs have a unique ability to target distant organs and effectively penetrate cellular organelles compared with LBPs (live microbes), which are generally restricted to the mucosal or skin surface. Moreover, microbial EVs can be conveniently administered orally or topically, as opposed to biologics requiring intravenous infusion or subcutaneous injection. Among the candidates for next-generation biological therapies, microbial EVs offer a variety of advantages over live microbes (LBPs), parabiotics, and exosomes (human cell EVs) in terms of pharmacology (pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics), safety, and CMC (characterization, manufacturing, and quality control).
Microbial EV Therapy as a Smart Natural Drug
Value Propositions of Microbial EV Therapy:
- Smart drug delivery system
- Target undruggable targets
- Innovative mode of action (MoA)
- Convenient administration
- Minimal adverse drug reactions
- Reasonable production cost
Customer reviews
No reviews were found for Microbial EV Nanotherapeutics. Be the first to review!