Fluidda - Functional Respiratory Imaging (FRI) Technology
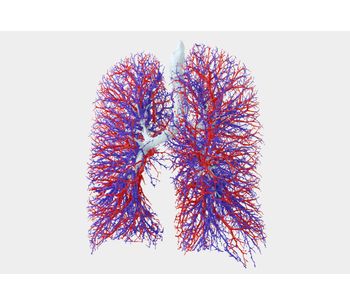
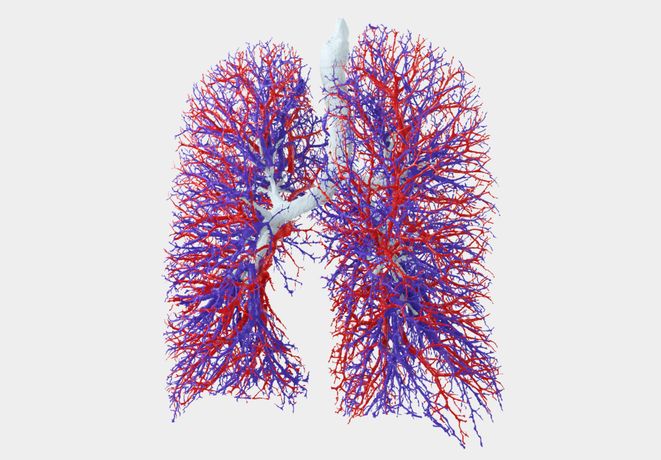
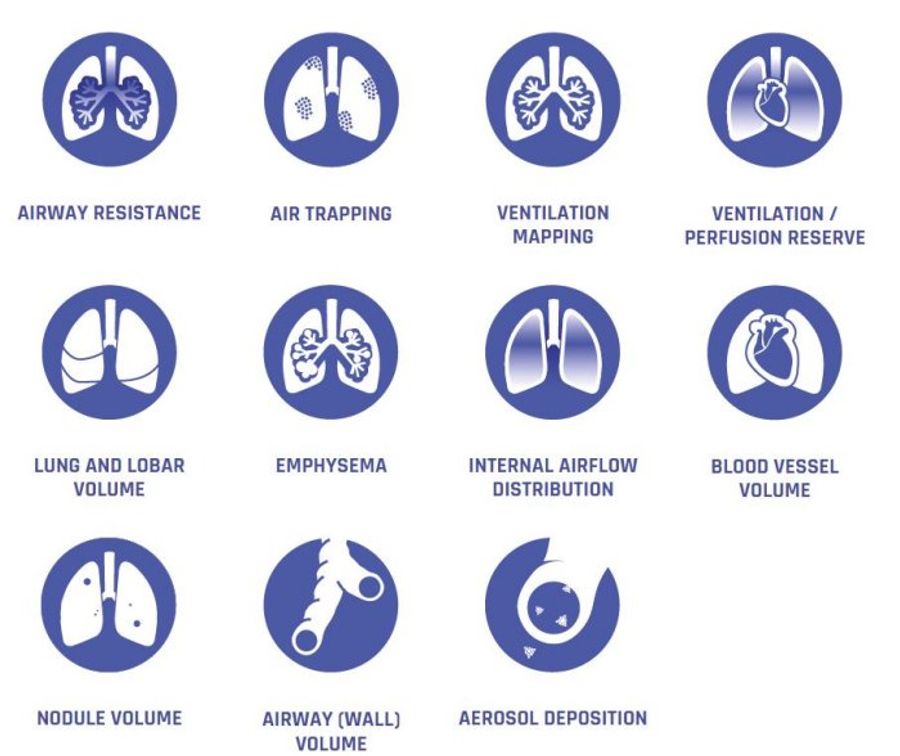
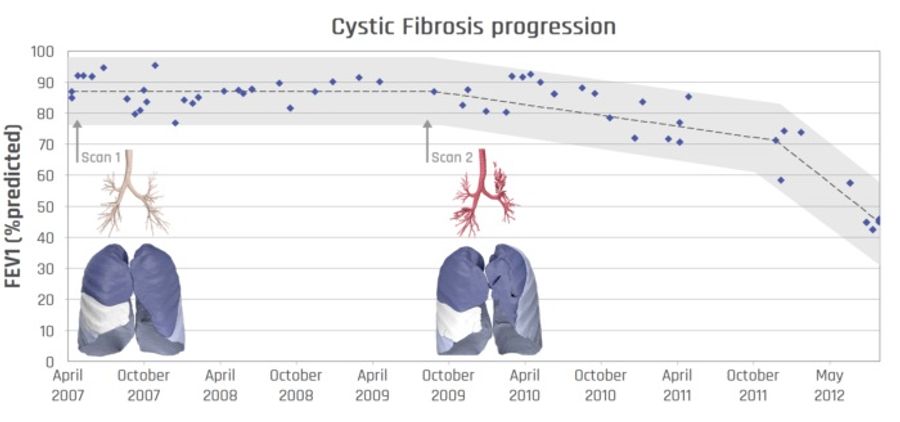
Traditional lung function measurements, such as FEV1 or FVC, only provide meaningful information about the condition of the entire lung and do not indicate where the exhaled air is coming from. Regional information is often crucial to understand the pathophysiology of the individual patient and to give guidance for optimal treatment. Functional Respiratory Imaging (FRI) is a clinically meaningful and non-invasive measurement of the patient-specific respiratory system. A set of distinct biomarkers analyzes exposure, structure and function of the lungs and airways in any respiratory disease.
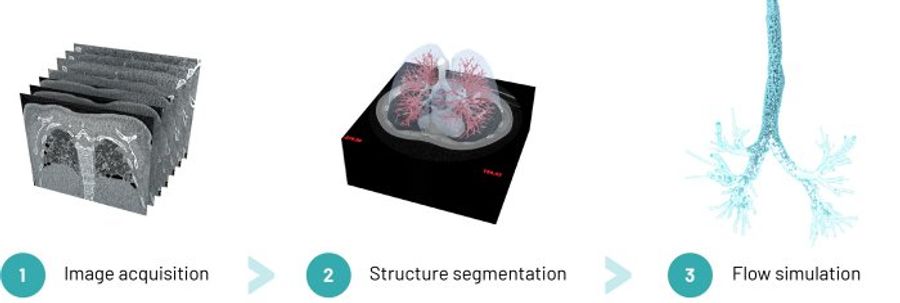
THE FRI PROCESS CONSISTS OF THREE PHASES:
PHASE 1: MEDICAL IMAGING
The process starts with the acquisition of low dose, high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scans of the patient.
PHASE 2: IMAGE PROCESSING
Measurements are performed on the segmented 3-dimensional geometries from these scans.
PHASE 3: FLOW SIMULATION
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is used to quantify airflow and exposure to inhaled particles.
Traditional lung function measurements, such as FE...
Traditional lung function measurements, such as FEV1 or FVC, only provide meaningful information about the condition of the entire lung and do not indicate where the exhaled air is coming from.
Regional information is often crucial to understand the pathophysiology of the individual patient and to give guidance for optimal treatment.
Sensitive biomarkers which measure lung disease stage and the biological response to treatment are needed to facilitate clinical development decisions, accelerate drug development and improve patient care.
Therefore, FRI is an essential addition to the toolkit of research and clinical practice in respiratory diseases.
Customer reviews
No reviews were found for Fluidda - Functional Respiratory Imaging (FRI) Technology. Be the first to review!