Breath Biopsy - Biomarkers on Exhaled Breath
From Science & Technology
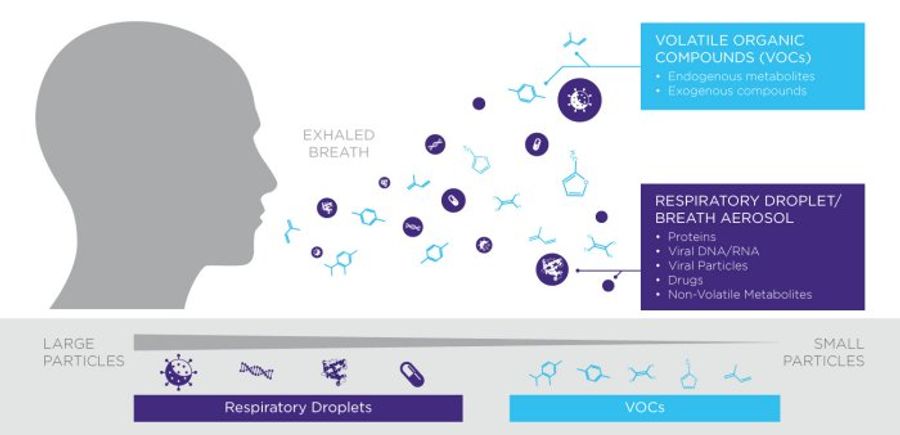
Non-invasive analysis of biomarkers on breath in early detection and precision medicine. Exhaled breath is more than just air, it contains over 1,000 volatile organic compounds (VOCs) as well as microscopic aerosol particles, also known as respiratory droplets, originating from the lungs and airways. Both VOCs and breath aerosol represent rich sources of biological information. Breath Biopsy provides an entirely new way to access this information by collecting and analyzing breath samples.
What is Breath Biopsy?
This makes it possible to:
- Investigate biomarkers for disease early detection
- Stratify patients by phenotype for precision medicine
- Detect and monitor response to treatments
- Measure exposure to hazardous substances and their impact on the body
Unlike liquid and tissue biopsies, which require blood or tissue samples to be taken, Breath Biopsy provides a completely non-invasive solution that maximizes patient comfort.
What are Breath Biomarkers?
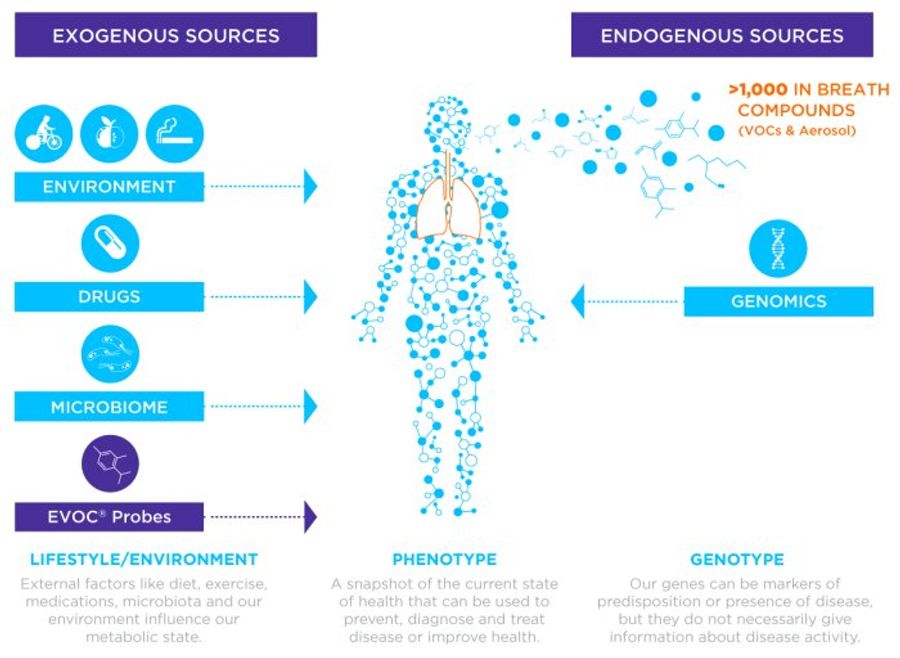
Breath biomarkers largely arise either as VOCs captured from the air or as non-volatiles found within respiratory droplets from exhaled breath aerosols. Both sources are of great interest for research and medical applications as they provide complementary information. Many exhaled VOCs are the products of metabolism and so reflect biochemical activities within the body.
Respiratory droplets can contain non-volatile metabolites, proteins, DNA and viral pathogens offering insights into other biological processes. Both sample types can also be sources of data relating to environmental factors such as pollutants and chemical exposures that can have impacts on long-term health.
Due to their volatile nature, VOCs in breath are t...
Due to their volatile nature, VOCs in breath are typically small molecules. They can arise from both external sources (food, smoking, pollution, chemicals) and from within the body itself, as such they can reflect biochemical and metabolic activity as well as environmental effects. Endogenous VOCs are often the product of metabolic processes and, as such, the metabolic effects of diseases are reflected in the pattern of exhaled VOCs. Samples are typically analyzed and VOCs identified using detailed chemical analysis tools such as mass spectrometry. Non-invasive Breath Biopsy represents an adaptable and accessible means to detect and measure VOCs as biomarkers for disease.
By contrast, exhaled aerosols contain a range of larger particles of potential clinical relevance including non-volatile metabolites, proteins, nucleotides, and even whole viruses, which are also suitable for non-invasive collection and analysis. Depending on the biomarker, a range of additional analytical solutions are available, such as antibody-based assays, PCR and DNA sequencing as well as liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS).
Customer reviews
No reviews were found for Breath Biopsy - Biomarkers on Exhaled Breath. Be the first to review!